mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
After successful installation of MDriven on the Ubuntu Server, this installation also ensured we installed Nginx Web server to create the /var/www/ directory. | After successful installation of MDriven on the Ubuntu Server, this installation also ensured we installed Nginx Web server to create the /var/www/ directory. | ||
Now check the status of | Now check the status of Nginx service using the command.<syntaxhighlight> | ||
service nginx status | service nginx status | ||
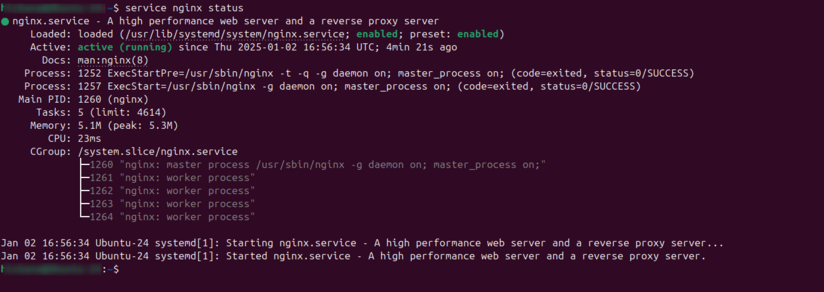
</syntaxhighlight>The result should be as shown below with Active: active (running) which indicates that Nginx service is up and running. | </syntaxhighlight>The result should be as shown below with Active: active (running) which indicates that Nginx service is up and running. | ||
[[File:Documentation Serving MDriven with Nginx Server as a Proxy 1735837499808.png| | [[File:Documentation Serving MDriven with Nginx Server as a Proxy 1735837499808.png|thumb|824x824px|none]]If Nginx is not running, you can start the service with the command<syntaxhighlight> | ||
service nginx start | service nginx start | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -1: Configure Nginx ===== | |||
Navigate to the Nginx directory where we will create a configuration file for MDriven Turnkey and the MDriven Server<syntaxhighlight> | |||
Navigate to the | |||
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available | cd /etc/nginx/sites-available | ||
</syntaxhighlight>The “/etc/nginx/sites-available” directory typically contains configuration files for Nginx virtual hosts. Each file in this directory represents a separate virtual host configuration, allowing you to define settings for different websites or applications hosted on your server. There will be a default config file available already. You can remove it or leave it as is. | </syntaxhighlight>The “/etc/nginx/sites-available” directory typically contains configuration files for Nginx virtual hosts. Each file in this directory represents a separate virtual host configuration, allowing you to define settings for different websites or applications hosted on your server. There will be a default config file available already. You can remove it or leave it as is. | ||
===== Step -2: Create a configuration file for MDriven Server ===== | |||
<syntaxhighlight> | |||
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdrivenserver | sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdrivenserver | ||
</syntaxhighlight>Copy and paste the below content in the file. Replace IP_ADDRESS_OR_DOMAIN_NAME with correct IP address or domain name pointing to your MDriven Server.<syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight>Copy and paste the below content in the file. Replace IP_ADDRESS_OR_DOMAIN_NAME with correct IP address or domain name pointing to your MDriven Server.<syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 42: | ||
access_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_server_access.log; | access_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_server_access.log; | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -3: Enable the site and restart Nginx ===== | |||
<syntaxhighlight> | |||
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdrivenserver /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ | sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdrivenserver /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ | ||
sudo nginx -t # Test configuration | sudo nginx -t # Test configuration | ||
sudo systemctl restart nginx | sudo systemctl restart nginx | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -4: Now, you can access MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey. ===== | |||
Enter the following URL respectively"http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:5042" - in this case it will be <nowiki>http://10.0.2.15:5042</nowiki> | |||
===== Step -5: Create a configuration file for MDriven Turnkey ===== | |||
<syntaxhighlight> | |||
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdriventurnkey | sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdriventurnkey | ||
</syntaxhighlight>Copy and paste the below content in the file. Replace IP_ADDRESS_OR_DOMAIN_NAME with correct IP address or domain name pointing to your MDriven Server<syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight>Copy and paste the below content in the file. Replace IP_ADDRESS_OR_DOMAIN_NAME with correct IP address or domain name pointing to your MDriven Server<syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 82: | ||
access_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_turnkey_access.log; | access_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_turnkey_access.log; | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -6: Enable the site and restart Nginx ===== | |||
<syntaxhighlight> | |||
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdriventurnkey /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ | sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdriventurnkey /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ | ||
sudo nginx -t | sudo nginx -t | ||
sudo systemctl restart nginx | sudo systemctl restart nginx | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -7: Access MDriven Turnkey ===== | |||
Now, you can access MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey by entering the following URL respectively"http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:5042" in this case it will be <nowiki>http://10.0.2.15:5011</nowiki> | Now, you can access MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey by entering the following URL respectively"http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:5042" in this case it will be <nowiki>http://10.0.2.15:5011</nowiki> | ||
With our current installation setup, MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey are still running using HTTP: We can proceed to secure our production setup using HTTPS instead. To secure our Nginx proxy server setup, follow the steps below: | With our current installation setup, MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey are still running using HTTP: We can proceed to secure our production setup using HTTPS instead. To secure our Nginx proxy server setup, follow the steps below: | ||
===== Step -1: Install Certbot and Nginx Plugin ===== | |||
<syntaxhighlight> | |||
sudo apt update | sudo apt update | ||
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx | sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -2: Ensure Nginx is running. ===== | |||
<syntaxhighlight> | |||
sudo systemctl start nginx | sudo systemctl start nginx | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -3: Obtain an SSL Certificate. ===== | |||
Run Certbot with the Nginx plugin to automatically configure SSL:<syntaxhighlight> | Run Certbot with the Nginx plugin to automatically configure SSL:<syntaxhighlight> | ||
sudo certbot --nginx | sudo certbot --nginx | ||
| Line 101: | Line 113: | ||
Select the domain name to secure (e.g., 10.0.2.15 or your custom domain). | Select the domain name to secure (e.g., 10.0.2.15 or your custom domain). | ||
Certbot will generate and configure the SSL certificate automatically. | Certbot will generate and configure the SSL certificate automatically. | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -4: Verify the SSL Configuration. ===== | |||
Certbot updates your Nginx configuration to SSL. However, manually verify that the changes are correct. Your updated configuration should look like this:<syntaxhighlight> | Certbot updates your Nginx configuration to SSL. However, manually verify that the changes are correct. Your updated configuration should look like this:<syntaxhighlight> | ||
server { | server { | ||
| Line 147: | Line 160: | ||
</syntaxhighlight>Restart Nginx:<syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight>Restart Nginx:<syntaxhighlight> | ||
sudo systemctl restart nginx | sudo systemctl restart nginx | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== Step -6: Automatic Certificate Renewal. ===== | |||
Let's Encrypt certificates are valid for 90 days, but Certbot automatically renews them. Add a cron job to test renewal periodically:<syntaxhighlight> | Let's Encrypt certificates are valid for 90 days, but Certbot automatically renews them. Add a cron job to test renewal periodically:<syntaxhighlight> | ||
Open the crontab editor: | Open the crontab editor: | ||
Revision as of 05:23, 7 January 2025
After successful installation of MDriven on the Ubuntu Server, this installation also ensured we installed Nginx Web server to create the /var/www/ directory.
Now check the status of Nginx service using the command.
service nginx statusThe result should be as shown below with Active: active (running) which indicates that Nginx service is up and running.
If Nginx is not running, you can start the service with the command
service nginx startStep -1: Configure Nginx
Navigate to the Nginx directory where we will create a configuration file for MDriven Turnkey and the MDriven Server
cd /etc/nginx/sites-availableThe “/etc/nginx/sites-available” directory typically contains configuration files for Nginx virtual hosts. Each file in this directory represents a separate virtual host configuration, allowing you to define settings for different websites or applications hosted on your server. There will be a default config file available already. You can remove it or leave it as is.
Step -2: Create a configuration file for MDriven Server
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdrivenserverCopy and paste the below content in the file. Replace IP_ADDRESS_OR_DOMAIN_NAME with correct IP address or domain name pointing to your MDriven Server.
server {
listen 80;
server_name 10.0.2.15; #---domain-name or IP address
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5042; # Replace with Mono server's port
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_read_timeout 300;
proxy_connect_timeout 300;
proxy_redirect off;
}
location ~* \.(css|js|jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|otf|eot|html|htm)$ {
root /var/www/html/mdriven;
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
error_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_server_error.log;
access_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_server_access.log;
}Step -3: Enable the site and restart Nginx
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdrivenserver /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t # Test configuration
sudo systemctl restart nginxStep -4: Now, you can access MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey.
Enter the following URL respectively"http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:5042" - in this case it will be http://10.0.2.15:5042
Step -5: Create a configuration file for MDriven Turnkey
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdriventurnkeyCopy and paste the below content in the file. Replace IP_ADDRESS_OR_DOMAIN_NAME with correct IP address or domain name pointing to your MDriven Server
server {
listen 8000;
server_name 10.0.2.15; #---domain-name or IP address
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5011; # Replace with Mono server's port
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_read_timeout 300;
proxy_connect_timeout 300;
proxy_redirect off;
}
location ~* \.(css|js|jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|otf|eot|html|htm)$ {
root /var/www/html/mdriven;
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
error_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_turnkey_error.log;
access_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_turnkey_access.log;
}Step -6: Enable the site and restart Nginx
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mdriventurnkey /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxStep -7: Access MDriven Turnkey
Now, you can access MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey by entering the following URL respectively"http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:5042" in this case it will be http://10.0.2.15:5011
With our current installation setup, MDriven Server and MDriven Turnkey are still running using HTTP: We can proceed to secure our production setup using HTTPS instead. To secure our Nginx proxy server setup, follow the steps below:
Step -1: Install Certbot and Nginx Plugin
sudo apt update
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginxStep -2: Ensure Nginx is running.
sudo systemctl start nginxStep -3: Obtain an SSL Certificate.
Run Certbot with the Nginx plugin to automatically configure SSL:
sudo certbot --nginxFollow the prompts:
Select the domain name to secure (e.g., 10.0.2.15 or your custom domain).
Certbot will generate and configure the SSL certificate automatically.Step -4: Verify the SSL Configuration.
Certbot updates your Nginx configuration to SSL. However, manually verify that the changes are correct. Your updated configuration should look like this:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name 10.0.2.15; # Replace with your domain or IP
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/10.0.2.15/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/10.0.2.15/privkey.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5011;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_read_timeout 300;
proxy_connect_timeout 300;
proxy_redirect off;
}
location ~* \.(css|js|jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|otf|eot|html|htm)$ {
root /var/www/html/mdriven;
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
error_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_turnkey_error.log;
access_log /var/log/nginx/mdriven_turnkey_access.log;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 10.0.2.15;
# Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}Test the configuration:
sudo nginx -tRestart Nginx:
sudo systemctl restart nginxStep -6: Automatic Certificate Renewal.
Let's Encrypt certificates are valid for 90 days, but Certbot automatically renews them. Add a cron job to test renewal periodically:
Open the crontab editor:
sudo crontab -e
Add the following line to test renewal daily:
0 0 * * * certbot renew --quiet && systemctl reload nginx